ผู้ผลิตแบริ่งลูกกลิ้งชั้นนำปี 2025: คู่มือฉบับสมบูรณ์
1. Introduction
Roller bearings are fundamental, yet critical, components in virtually all rotating machinery across every industrial sector. They facilitate motion by reducing friction between moving parts, supporting radial and/or axial loads, and ensuring the smooth, efficient operation of everything from car wheels and conveyor systems to massive wind turbines and heavy-duty industrial gearboxes. Without highly reliable bearings, industrial machinery would quickly fail due to excessive heat, wear, and power loss. Their quality and precision are paramount to the longevity and performance of any machine.
The global demand for high-performance bearings has led to the rise of several multinational corporations that dominate the manufacturing landscape. Choosing the right supplier is as important as selecting the correct bearing type.
Purpose of This Guide
The purpose of this comprehensive guide is to identify and discuss the top roller bearing manufacturers in the world. We will provide an overview of the industry leaders, examine their key product strengths, and, most importantly, detail the essential factors you must consider when selecting a supplier for your standard or custom non-standard bearing needs. This information is vital for engineers, procurement specialists, and maintenance professionals seeking the best bearings for their specific applications.
| Key Takeaway | Impact on Machinery |
|---|---|
| Friction Reduction | Increased efficiency and less heat generation. |
| Load Support | Enables machinery to handle high radial and axial forces. |
| Precision & Quality | Guarantees extended service life and reliable operation. |
2. What are Roller Bearings?
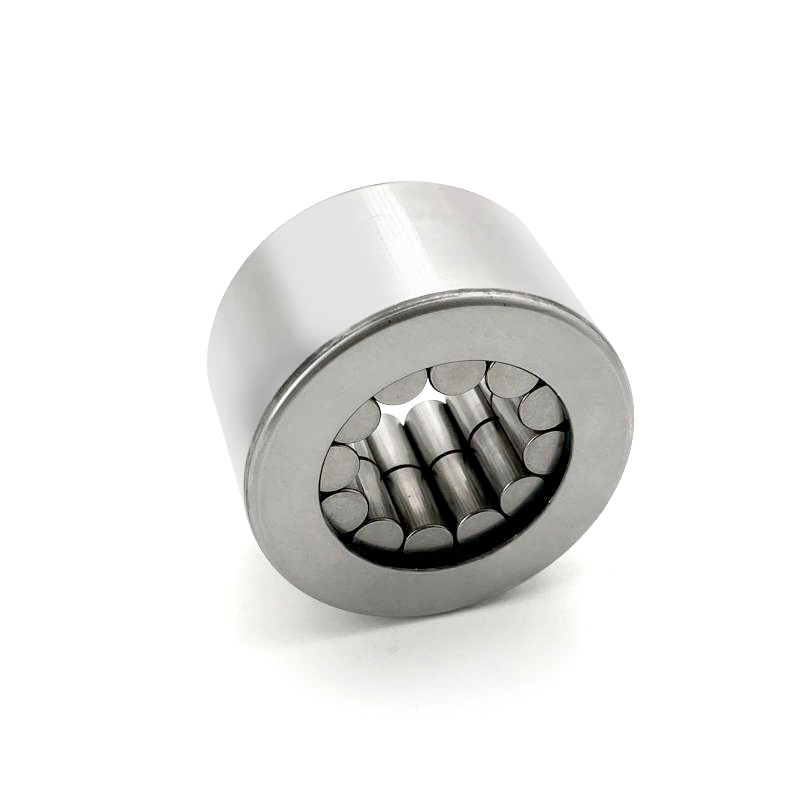
A roller bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that utilizes cylindrical, tapered, or spherical rolling elements to maintain the separation between moving parts (races) to reduce rotational friction and support loads.
How Roller Bearings Work
Roller bearings consist of three main components:
- Inner and Outer Rings (Races): These provide the pathways (raceways) for the rolling elements.
- Rolling Elements (Rollers): These are the cylinders, needles, cones, or spheres that carry the load.
- Cage or Retainer: This spaces the rollers evenly and prevents them from coming into contact with one another.
When a load is applied, the rollers distribute the force across a larger contact area than point-contact bearings, allowing them to support significantly higher radial and combined (radial and axial) loads . The rolling motion replaces sliding friction, dramatically reducing energy consumption and heat generation in the machinery.
Roller Bearings vs. Ball Bearings
While both roller bearings and ball bearings are rolling-element bearings designed to minimize friction, they differ primarily in the geometry of their rolling elements and the type of load they can best handle.
| Feature | Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Element Shape | Cylinders, cones, or spheres (rollers). | Spheres (balls). |
| Contact Type | Line contact (or large elliptical contact). | Point contact (or small elliptical contact). |
| Load Capacity | Higher load capacity (especially radial load). | Lower to moderate load capacity. |
| Suitability | Heavy-duty, slow to medium-speed applications. | High-speed, lower-load applications. |
Types of Roller Bearings
The type of roller bearing is defined by the shape of its rolling elements, each suited for distinct load types and application geometries.
* Tapered Roller Bearings
These bearings use truncated cones (tapered rollers) and raceways. They are uniquely designed to manage high combined radial and axial loads . They are commonly used in pairs (or sets) and are essential in applications like automotive wheel hubs, transmissions, and gear drives.
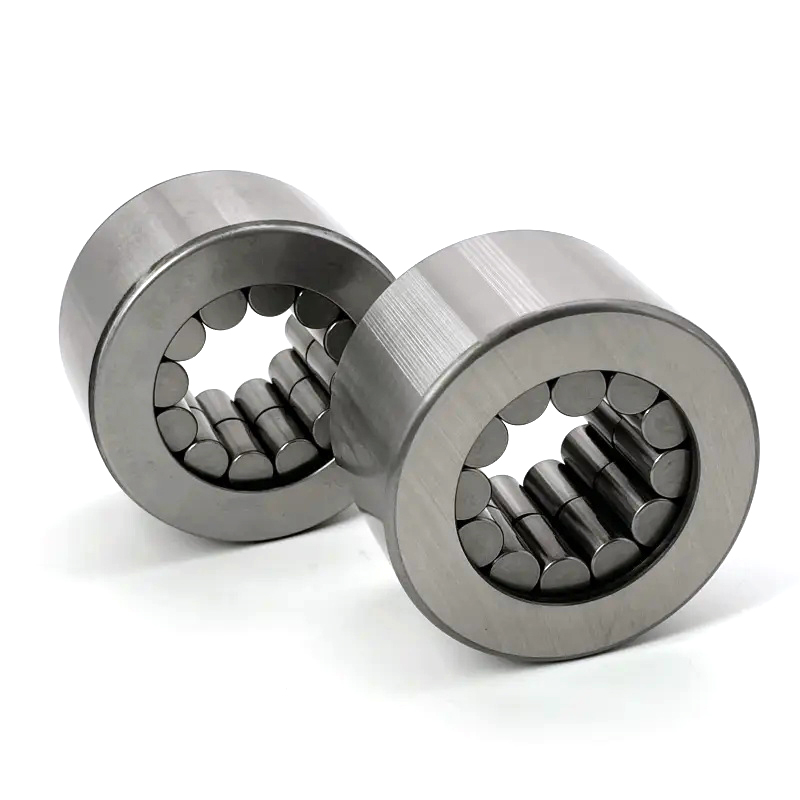
* Cylindrical Roller Bearings
These feature cylindrical rollers where the length is typically greater than the diameter. The rollers have line contact with the raceways, enabling them to handle very high radial loads . They generally cannot accommodate significant axial load. They are frequently used in large electric motors, pumps, and gearboxes.
* Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings have two rows of barrel-shaped or spherical rollers in an outer ring that has a spherical raceway. This design allows the bearing to self-align and tolerate substantial misalignment or shaft deflection without compromising performance, making them ideal for challenging environments like mining, construction, and wind power applications. They handle heavy radial and moderate axial loads.
* Needle Roller Bearings
These are a variation of the cylindrical roller bearing but use rollers that are exceptionally thin and long ( “needle-like” ). This design provides a very high load-carrying capacity relative to their cross-section, making them ideal for applications with extremely limited radial space, such as automotive transmissions, universal joints, and small engines.
3. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Roller Bearing Manufacturer
Selecting the right manufacturer is a strategic decision that directly impacts the performance, maintenance costs, and lifespan of your machinery. As a custom non-standard bearing manufacturer, we understand that quality and reliability are non-negotiable.
Here are the critical factors to evaluate when choosing a roller bearing supplier:
* Quality and Reliability
This is the most crucial factor. A top manufacturer uses high-grade materials (e.g., specialized steel alloys) and maintains strict tolerances during manufacturing. Poorly manufactured bearings can lead to premature failure, costly downtime, and even catastrophic equipment damage. Look for a proven track record of durability and low failure rates, particularly in demanding applications.
* Range of Products Offered
While your current need might be for a specific roller bearing type, a comprehensive manufacturer offers a wide portfolio. This ensures they possess broad expertise and can provide optimal solutions for future needs, including a full spectrum of:
- Standard catalog bearings (ISO, DIN, etc.)
- High-precision bearings
- Sealed and lubricated-for-life variants
- Customization options (crucial for non-standard applications).
* Customization Options
For non-standard or highly specialized applications (like custom machinery or extreme environments), the ability to modify or completely custom-design a bearing is essential. A flexible manufacturer can adjust:
- Internal geometry and clearance
- Cage and roller materials
- Surface coatings and treatments
- Integrated sealing solutions
* Technical Support and Expertise
The manufacturer should offer robust engineering support throughout the design and operational lifecycle. This includes assistance with:
- Bearing selection and calculation (e.g., fatigue life, static and dynamic load ratings).
- Installation and maintenance procedures.
- Failure analysis to diagnose and prevent future issues.
- Access to advanced simulation and modeling tools.
* Price and Availability
While price should not override quality, it is a practical consideration. Look for a supplier that offers a competitive price-to-performance ratio. Furthermore, global distribution and localized inventory are vital to minimize lead times, especially for critical replacement parts.
* Certifications and Standards (e.g., ISO 9001)
Verify that the manufacturer adheres to recognized international quality management standards. Key certifications include:
| Standard | Focus Area | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems (QMS) | Demonstrates a commitment to meeting customer and regulatory requirements. |
| ISO/TS 16949 | Automotive Sector (I.A.T.F. 16949) | Required for suppliers to the automotive industry, emphasizing process quality. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Shows commitment to sustainable manufacturing practices. |
4. Top Roller Bearing Manufacturers
While the global market is dominated by several large multinational companies, specialized manufacturers like yours provide crucial niche expertise, especially in non-standard and high-precision segments.
* FTM (Shaoxing Shangyu Flight Seiko Machinery Co., Ltd.)
| Key Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Established | 2006 (Built upon 30 years of technical design experience) |
| Focus | R&D, manufacturing, and customization of non-standard and high-precision bearings (import substitution). |
| Unique Strength | Deep expertise in non-standard bearing solutions, guided by a Ph.D. in Tribology. |
| Key Markets | Engineering Machinery, Textile Machinery, and various domestic and international fields. |
Overview of the Company:
Founded in 2006, FTM (Shaoxing Shangyu Flight Seiko Machinery Co., Ltd.) distinguishes itself as an agile, technology-driven enterprise. Our core mission is the R&D, manufacturing, and customization of bespoke bearing solutions, focusing particularly on non-standard bearings and high-precision bearings designed for import substitution. With over three decades of accumulated technical design experience, FTM has established an outstanding reputation for quality.
Key Products and Services:
- Custom Non-Standard Bearings: Tailored solutions where standard catalog products are insufficient.
- High-Precision Bearings: Manufacturing excellence aiming for import substitution quality.
- Bearing Accessories and Mechanical Parts: Comprehensive support for rotating equipment.
- Consulting & Design: Professional technical team providing high-quality bearing solutions backed by a Doctor of Tribology guiding product research.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (FTM) | Weaknesses (FTM) |
|---|---|
| Customization Expertise: Exceptional capability in specialized non-standard and high-precision designs. | Market Penetration: Smaller global distribution network compared to the multinational giants. |
| Technical Excellence: Over 30 years of experience; R&D guided by a Ph.D. in Tribology. | Standard Catalog Range: Primary focus is customization, not mass production of standard off-the-shelf bearings. |
| Quality Manufacturing: Introduction of advanced CNC machine tools from Japan ensures stability and high processing accuracy. | Brand Recognition: Still developing the global brand recognition that comes with decades of multinational operations. |
* SKF (Svenska Kullagerfabriken)
Overview of the Company:
A Swedish company founded in 1907, SKF is arguably the largest and most recognizable name in the bearing industry. They are a true knowledge engineering company, offering products and services related to rotating equipment performance across virtually every industry.
Key Products and Services:
- Roller bearings (Spherical, Cylindrical, Tapered, Needle)
- Seals, lubrication systems, and maintenance products
- Condition monitoring and asset management services
- SKF Explorer class bearings (High-performance, increased service life)
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (SKF) | Weaknesses (SKF) |
|---|---|
| Global Reach: Unmatched distribution and service network worldwide. | Cost: Often positioned at the premium end of the price spectrum. |
| Innovation: Industry leader in smart bearings and condition monitoring technology. | Lead Time: Certain specialized or custom products can have long lead times due to global demand. |
| Product Breadth: Offers a complete “rotating shaft” solution, including related tools and maintenance. |
* Schaeffler Group (INA/FAG)
Overview of the Company:
A German industrial powerhouse, the Schaeffler Group encompasses the globally recognized brands INA and FAG. FAG focuses on high-precision ball and roller bearings, while INA specializes in needle roller bearings and linear technology.
Key Products and Services:
- FAG: Large, high-precision roller bearings, spherical, and cylindrical types.
- INA: Industry-leading needle roller bearings, cam followers, and linear systems.
- Automotive (e-mobility and chassis systems) and Industrial components.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (Schaeffler) | Weaknesses (Schaeffler) |
|---|---|
| Precision: Highly regarded for German engineering and manufacturing quality, particularly FAG high-precision lines. | Complexity: The dual-brand structure (INA/FAG) can sometimes complicate product selection for new users. |
| Needle Bearings: INA is considered the gold standard in needle roller bearing technology. | |
| Automotive Strength: Deep integration and leading technology in the automotive sector. |
* NSK Ltd.
Overview of the Company:
A major Japanese manufacturer, NSK (Nippon Seiko Kabushiki Kaisha) is a global supplier of bearings, automotive components, and precision machinery and parts. They are known for their strong focus on environmental sustainability and product longevity.
Key Products and Services:
- Standard and high-precision roller bearings (Cylindrical, Tapered, Spherical)
- Mega-Torque Motors and Actuators
- Advanced sealing technologies (e.g., DDL sealed bearings)
- Automotive steering and powertrain components.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (NSK) | Weaknesses (NSK) |
|---|---|
| Quality & Quiet Operation: Known for extremely smooth, quiet-running, and highly durable bearings. | Price: Tends to be positioned similarly to SKF and Schaeffler in the premium category. |
| Precision Machinery: Strong expertise in bearings for machine tool applications demanding extremely high accuracy. | |
| Global Manufacturing: Operates a vast network of production facilities worldwide. |
* JTEKT Corporation (Koyo)
Overview of the Company:
Koyo is the bearing brand of the Japanese JTEKT Corporation. JTEKT is a massive company formed from the merger of Koyo Seiko and Toyoda Machine Works, with strong roots in machine tools and steering systems.
Key Products and Services:
- Wide range of roller bearings (Tapered, Cylindrical, Spherical)
- Automotive steering systems (a major global market share leader)
- Advanced machine tool spindle bearings
- Sealed and protected bearings for harsh environments.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (Koyo) | Weaknesses (Koyo) |
|---|---|
| Tapered Bearings: Historically very strong in automotive and industrial tapered roller bearings. | Visibility: The Koyo brand can sometimes be overshadowed by the larger JTEKT corporate identity. |
| High Load Capacity: Known for robust bearings designed for heavy industrial use. | |
| Mass Production Efficiency: Excellent at delivering consistent quality in high-volume production runs. |
* Timken Company
Overview of the Company:
An American company established in 1899, Timken is globally synonymous with tapered roller bearings , a technology they pioneered. While they have diversified, this remains a core strength.
Key Products and Services:
- Tapered Roller Bearings (SET—Single-Row, Engineered Tapered)
- Spherical Roller Bearings and Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- Power Transmission Products (Gears, Couplings, Belts, Chains)
- Engineered steel and alloy materials (historically a major strength).
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (Timken) | Weaknesses (Timken) |
|---|---|
| Tapered Bearings: Undisputed market leader and expert in tapered roller technology. | Range: Historically more focused on roller bearings than the comprehensive ball bearing range of their competitors. |
| Engineered Materials: Deep expertise in metallurgy ensures high-performance materials. | |
| Heavy Industry: Strong market presence in industries like rail, mining, and aerospace. |
* NTN Corporation
Overview of the Company:
Another major Japanese bearing manufacturer, NTN is a key global supplier of both bearings and constant velocity joints (CVJs) for the automotive sector. They focus heavily on lightweight and low-torque bearings.
Key Products and Services:
- Spherical Roller Bearings (Ultage Series)
- Integrated products combining bearings with sensors
- High-performance precision bearings for specialized machinery
- CVJs and other automotive components.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
| Strengths (NTN) | Weaknesses (NTN) |
|---|---|
| Innovation: Focus on developing new materials and designs for energy-efficient operation. | Public Profile: Sometimes perceived as slightly less visible than SKF or Schaeffler, despite its large size. |
| Automotive Expertise: A critical global supplier to the automotive industry for high-reliability components. |
* Others (Smaller/Niche Manufacturers)
Beyond the “Big Six” global players, smaller, specialized companies play a vital role, often excelling in niche or extremely high-tolerance applications:
- RBC Bearings: Known for highly engineered, critical bearings used in aerospace and defense.
- McGill (Emerson/Regal Beloit): Traditionally strong in specialized cam followers and mounted bearings.
- Aurora Bearing Company: Specializes in rod ends and spherical plain bearings.
5. Product Focus (Leading Examples)
This section showcases specific roller bearing product series offered by the market leaders, demonstrating their expertise in particular bearing types and applications, including the crucial area of bespoke solutions.
| Bearing Type | Manufacturer | Product Series Example | Key Feature / Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Roller Types | FTM (Shaoxing Shangyu Flight) | Non-Standard & High-Precision Custom Bearings | Customization Focus: Specialized in import substitution and bespoke designs (clearance, material, geometry) for high-precision, specific-application machinery. |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Timken | SET (Single-Row, Engineered Tapered) | Engineered bearing geometry for maximum load-carrying capacity in a compact envelope. Timken’s proprietary design expertise. |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | SKF | Explorer Class Tapered Bearings | Improved steel purity and optimized surface finish for reduced friction and extended service life. Suitable for high-stress applications. |
| Cylindrical Roller Bearings | Schaeffler Group (FAG) | High-Precision Cylindrical Roller Bearings | Extremely tight radial runout tolerances and high-speed capabilities, often used in machine tool spindles. |
| Cylindrical Roller Bearings | NSK Ltd. | EM Series Cylindrical Roller Bearings | High load capacity and excellent durability. Features an optimized internal design and a specialized cage for high rotational speeds. |
| Spherical Roller Bearings | SKF | Explorer Spherical Roller Bearings | Patented internal design improves load distribution and reduces friction, resulting in up to 3x longer service life than standard designs. |
| Spherical Roller Bearings | NTN Corporation | Ultage Spherical Roller Bearings | NTN’s high-performance bearing series featuring optimized roller profiles and advanced materials for high reliability and shock load resistance. |
| Needle Roller Bearings | Schaeffler Group (INA) | INA Needle Roller Bearings (Various Series) | Industry benchmark for compactness and high load capacity in small radial spaces. Includes drawn cup and machined ring designs. |
| Needle Roller Bearings | JTEKT (Koyo) | Koyo Needle Roller Bearings | Robust designs, often featuring labyrinth seals and specialized heat treatment for high contamination resistance and durability in industrial gearboxes. |
6. Applications of Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are the hidden workhorses that enable motion and reliability across virtually every major industrial sector. Their ability to handle high loads and shocks makes them indispensable in heavy and critical machinery.
* Automotive Industry
Roller bearings are crucial for safety, efficiency, and performance in vehicles. They manage the heavy loads and varying speeds associated with driving.
- Tapered Roller Bearings: Essential in wheel ends (hubs) and differentials to handle combined road and cornering forces.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Used in transmissions and gearboxes to support high radial loads from gear meshing.
- Needle Roller Bearings: Commonly found in transmissions, steering linkages, and universal joints where space is highly restricted.
* Aerospace Industry
In aircraft, bearings must operate under extreme conditions, including high speed, massive temperature fluctuations, and critical safety requirements.
- High-Precision Roller Bearings: Used in jet engine gearboxes and main shaft supports where precision and reliability are paramount.
- Specialized Materials: Bearings often use high-temperature steels or ceramics to maintain integrity at elevated operating temperatures and speeds.
* Industrial Machinery
This broad category encompasses almost all factory and processing equipment where continuous, heavy-duty operation is required.
- Mining and Construction: Spherical roller bearings are vital in conveyors, crushers, and earth-moving equipment because they tolerate heavy loads, shock, and misalignment caused by chassis flex.
- Pumps and Compressors: Cylindrical and angular contact roller bearings are used to ensure the precision and reliability of fluid handling systems.
- Metalworking: High-precision roller bearings are a core component of machine tool spindles where speed and micron-level accuracy are non-negotiable.
* Railroad Industry
Locomotives, freight cars, and passenger rail cars rely entirely on robust roller bearings to support immense weight and ensure continuous, safe operation.
- Tapered Roller Bearing Units (TRBUs): Specifically designed, integrated units used in railcar axles to provide easy installation and maintenance while handling extreme radial, axial, and shock loads.
* Wind Turbines
As a high-growth sector, wind power demands extremely large, durable, and reliable bearings that can last for decades in harsh, remote environments.
- Spherical and Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Used in the main shaft (supporting the rotor blades) and gearboxes to manage complex, cyclical loads and misalignment issues.
- Customization (FTM Focus): Given the unique scale and specific load characteristics, this sector frequently requires non-standard, high-precision custom bearings tailored to turbine design.
7. How to Select the Right Roller Bearing
Selecting the optimal roller bearing is a critical engineering process that involves evaluating the specific operating conditions and matching them to the bearing’s capabilities. A mismatch can lead to premature failure and costly downtime.
* Load Capacity
This is the single most important factor. Bearings are rated by two primary capacity types:
- Dynamic Load Rating ( C ): The constant radial load that a group of identical bearings can theoretically endure for a basic rating life of one million revolutions. This is used for applications with rotating loads.
- Static Load Rating ( C0 ): The load that corresponds to a total permanent deformation of the rolling element and race at the most heavily stressed contact point. This is used for applications with non-rotating loads, slow oscillation, or high static loads.
- Selection: The required load (dynamic or static) must always be less than or equal to the bearing’s rated capacity, often incorporating a safety factor.
* Speed Requirements
Bearings have a limiting speed or reference speed that they can operate at without excessive heat generation.
- High Speed: Generally favors smaller roller diameters, optimized cage designs, and high-precision tolerances (like FAG or NSK high-precision series).
- Low Speed/High Load: Focus shifts away from speed limitations toward maximizing static and dynamic load capacity.
* Operating Temperature
Extreme heat or cold affects the bearing’s material hardness, clearances, and lubricant life.
- High Temperature: Requires specialized materials, heat-stabilized steel, increased internal clearance, and high-temperature synthetic lubricants or solid lubricants.
- Selection: Ensure the bearing’s dimensional stability and performance are maintained throughout the entire operating temperature range.
* Lubrication
The choice of lubricant (grease or oil) and the method of delivery are paramount to managing friction and heat.
- Grease: Simpler, requires less maintenance, often used in sealed bearings (like NSK DDL sealed).
- Oil: Better for cooling, required for very high speeds and temperatures, often delivered via a circulating system.
- Re-lubrication Interval: Must be calculated based on speed, temperature, and bearing type to prevent lubrication failure, which is a leading cause of bearing malfunction.
* Environmental Conditions
The operating environment dictates the necessary protection features.
- Contamination: Applications in dirty or wet environments (e.g., mining, agriculture) require robust seals and shields to prevent abrasive particles or moisture from entering the raceways. FTM’s custom design capabilities are often leveraged here to develop specialized sealing solutions.
- Vibration and Shock: Requires bearings with features to withstand sudden, heavy impacts, such as reinforced cages and optimized internal geometry (e.g., Spherical Roller Bearings for high misalignment and shock).
| Selection Criterion | Key Consideration | Risk of Mismatch |
|---|---|---|
| Load | C (Dynamic) or C0 (Static) | Catastrophic failure due to material fatigue. |
| Speed | Limiting Speed, Cage Material | Overheating, lubricant breakdown, and early failure. |
| Environment | Contaminants, Misalignment | Abrasive wear, corrosion, and structural damage. |
8. Trends and Innovations in Roller Bearing Technology
The roller bearing industry is undergoing a digital and material science transformation, moving the component from a simple mechanical element to an intelligent enabler of Industry 4.0. These innovations are critical for meeting the demands of high-speed, high-precision, and sustainable machinery.
* Smart Bearings with Sensors
This is the most impactful trend, transitioning maintenance from reactive or preventive to predictive .
- Real-Time Condition Monitoring: Bearings are being fitted with embedded sensors (developed by companies like SKF and Schaeffler) that monitor critical parameters:
- Vibration (to detect early signs of wear or damage).
- Temperature (to indicate lubricant failure or excessive friction).
- Load and Speed.
- IoT Integration: The data collected is connected via the Internet of Things (IoT) to centralized control systems and AI-driven platforms, enabling accurate forecasting of bearing life and scheduling maintenance only when needed, dramatically reducing downtime and costs.
* Advanced Materials and Coatings
Innovation in material science is pushing the boundaries of bearing performance and durability.
- Hybrid Bearings: Combining traditional steel rings with ceramic rolling elements (e.g., silicon nitride). Ceramic elements are lighter, harder, non-conductive, and tolerate higher speeds and temperatures with less friction, making them ideal for electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains and machine tool spindles.
- Nanocoatings: The application of Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) , graphene, or other nanostructured coatings on bearing surfaces. These coatings significantly reduce friction, increase hardness, and provide exceptional resistance to corrosion and wear, even in environments with poor lubrication.
- Advanced Polymers: Using materials like PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) for cages to improve lubricant flow, reduce mass inertia, and enhance chemical resistance.
* Improved Lubrication Systems
Lubrication failure is the number one cause of bearing failure; therefore, innovation in this area is a priority.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings: Bearings featuring integrated solid lubricants or advanced grease reservoirs (like those developed by NTN and NSK) that ensure continuous supply without the need for external re-lubrication for the entire service life.
- Intelligent Lubrication Systems: Automated systems that use sensor data to deliver the precise amount of lubricant needed, based on actual operating conditions rather than fixed time intervals, maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
* Energy-Efficient Bearings
With a global focus on sustainability, manufacturers are prioritizing the reduction of energy losses in rotating equipment.
- Optimized Geometry: Bearings are designed with refined internal geometries (optimized roller and raceway profiles) and lower friction seals to minimize torque and energy consumption, contributing to the overall efficiency of the machinery.
- Lightweight Designs: The use of lighter materials, particularly in high-speed applications, reduces centrifugal forces and operating heat.
| Innovation | Core Benefit | Relevant Application |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Sensor Integration | Predictive Maintenance, Reduced Downtime | Wind Turbines, Automation, Rail. |
| Ceramic/Hybrid Materials | Higher Speed, Reduced Friction, Durability | EV Motors, High-Speed Spindles. |
| DLC/Nanocoatings | Superior Wear and Corrosion Resistance | Mining, Harsh Chemical Environments. |
| Custom 3D-Printed Parts | Intricate Geometries, Rapid Prototyping | Non-Standard/Bespoke Bearing Solutions (FTM focus). |
Conclusion
The successful operation of virtually all rotating machinery hinges upon the selection of the correct roller bearing and, critically, the manufacturer behind it. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the market, differentiating between the global giants and specialized solution providers.
Recap of Top Roller Bearing Manufacturers
The market is led by major players who offer vast catalogs, unparalleled global reach, and continuous innovation: SKF, Schaeffler Group (INA/FAG), NSK, JTEKT (Koyo), Timken, and NTN . Their strengths lie in high-volume, standardized, and proven high-performance products across all industrial sectors.
Crucially, companies like FTM (Shaoxing Shangyu Flight Seiko Machinery Co., Ltd.) fill the vital gap for unique and demanding specifications. Our focus on customization, non-standard bearings, and high-precision import substitution ensures that machinery with unique geometric, load, or environmental requirements can achieve maximum performance and longevity.
Importance of Choosing the Right Manufacturer
The selection process is more than a cost analysis; it is a partnership based on expertise. Whether your need is a high-volume standard part or a bespoke solution, the final choice should align with these priorities:
- Quality and Reliability: Must meet or exceed international standards (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Technical Fit: The manufacturer must demonstrate core competence in the required bearing type (e.g., Timken for Tapered, INA for Needle, or FTM for custom non-standard).
- Support: Access to engineering expertise and failure analysis is essential for optimizing machinery lifecycle.
By carefully considering the load, speed, temperature, and environmental factors outlined in this guide, and partnering with a manufacturer that possesses the necessary technical depth—whether for mass production or specialized customization—you ensure the highest degree of reliability for your critical assets.
We are confident that FTM’s 30 years of technical design experience and commitment to non-standard, high-precision solutions make us your best choice for tailored bearing requirements. Spin into eternity, inherit excellence, and create the future together.













 ดาวน์โหลดแคตตาล็อก
ดาวน์โหลดแคตตาล็อก
